Nearest Neighbor¶
This material is heavily based on the popular Standford CS231n lecture material. Please check on their website for more detailed information.
There are several repositories that offer solutions to CS231n problem sets, for examples:
https://github.com/lightaime/cs231n
https://github.com/mantasu/cs231n
https://github.com/jariasf/CS231n
Required Imports¶
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tqdm.auto import tqdm
plt.rcParams.update({
"text.usetex": True,
"font.family": "Times",
"font.size": 10,
})
from utils import *
Class KNearestNeighbor¶
Implementation of the naive version of the algorithm: compute the distances from the test dataset to all stored training dataset.
from utils import *
class KNearestNeighbor():
def train(self, X, y):
"""
- X: A 2D numpy array of shape (num_train, D) containing the training data
consisting of num_train samples each of dimension D.
- y: A 1D numpy array of shape (N,) containing the training labels, where
y[i] is the label for X[i].
"""
self.X_train = X
self.y_train = y
self.num_train = X.shape[0]
def predict(self, X, k=1, L=2):
"""
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data consisting
of num_test samples each of dimension D.
- k: The number of nearest neighbors that vote for the predicted labels.
- L: Determines how the distances are measured (L=1 means L1-norm and L=2
means L2-norm).
Returns:
- y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the
test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
dists = compute_distances(self.X_train, X, L=L)
y_pred = np.zeros(num_test, dtype=self.y_train.dtype)
for i in range(num_test):
closest_y = self.y_train[np.argsort(dists[i])][0:k]
v, n = np.unique(closest_y, return_counts=True)
y_pred[i] = v[np.argmax(n)]
return y_pred
Breast Cancer Wisconsin¶
We are going to use the breast cancer dataset that has been made publicly available.
The dataset was downloaded from this link
This dataset is also available as one of scikit-learn example datasets.
data = np.loadtxt("./datasets/breast_cancer/wdbc.data", delimiter=",", dtype=str)
X = np.float32(data[:, 2:]) # 30 dimensions
y = data[:, 1] # Diagnosis (M = malignant, B = benign)
print("Dimension numbers :", X.shape[1])
print("Number of data :", X.shape[0])
print("Labels :", np.unique(y))
Dimension numbers : 30
Number of data : 569
Labels : ['B' 'M']
Split the data:
70% for training
30% for testing
X_train = X[0:400, :]
y_train = y[0:400]
X_test = X[401:, :]
y_test = y[401:]
num_test = X_test.shape[0]
Train the Classifier¶
classifier = KNearestNeighbor()
classifier.train(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = classifier.predict(X_test, k=5, L=1)
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / float(num_test)
print('Got %d / %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))
Got 87 / 168 correct => accuracy: 0.517857
Cross Validations¶
Here, we perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k.
For each possible value of
k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithmnum_foldstimes.In each run, use all but one of the folds as training data. The unused fold is used as a validation set.
Store the accuracies for all fold and all values of
kin thek_to_accuraciesdictionary.
k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different
accuracy values that we found when using that value of k.
num_folds = 8
k_choices = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]
# Split up the training data into folds
X_train_folds = np.array_split(X, num_folds)
y_train_folds = np.array_split(y, num_folds)
# Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each
k_to_accuracies = {}
for k in k_choices:
k_to_accuracies[k] = []
for i in range(num_folds):
N = np.arange(num_folds)
N = np.delete(N, i)
X_train_temp = np.vstack([X_train_folds[j] for j in N])
y_train_temp = np.hstack([y_train_folds[j] for j in N])
# Train the classifier based on the training data
classifier.train(X_train_temp, y_train_temp)
# Predict using the remaining fold representing validation data
y_pred_temp = classifier.predict(X_train_folds[i], k=k, L=1)
# Compute the accuracy of the predicted label
num_correct = np.sum(y_pred_temp == y_train_folds[i])
k_to_accuracies[k].append(num_correct / len(y_pred_temp))
# Print out the computed accuracies
for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies):
accuracy = k_to_accuracies[k]
print('k = %d, average accuracy = %f, std accuracy = %f' % (k, np.mean(accuracy), np.std(accuracy)))
k = 1, average accuracy = 0.411067, std accuracy = 0.083290
k = 2, average accuracy = 0.490488, std accuracy = 0.060937
k = 3, average accuracy = 0.379524, std accuracy = 0.105952
k = 4, average accuracy = 0.402680, std accuracy = 0.086928
k = 5, average accuracy = 0.355022, std accuracy = 0.087927
k = 6, average accuracy = 0.381529, std accuracy = 0.083995
k = 7, average accuracy = 0.349839, std accuracy = 0.092521
k = 8, average accuracy = 0.367493, std accuracy = 0.081321
k = 9, average accuracy = 0.337490, std accuracy = 0.093599
k = 10, average accuracy = 0.348127, std accuracy = 0.093505
k = 11, average accuracy = 0.346293, std accuracy = 0.098788
k = 12, average accuracy = 0.348078, std accuracy = 0.095754
k = 13, average accuracy = 0.330350, std accuracy = 0.095045
k = 14, average accuracy = 0.328687, std accuracy = 0.094060
k = 15, average accuracy = 0.332086, std accuracy = 0.099775
# Plot the raw observations
for k in k_choices:
accuracies = k_to_accuracies[k]
plt.scatter([k] * len(accuracies), accuracies)
# plot the trend line with error bars that correspond to standard deviation
accuracies_mean = np.array([np.mean(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())])
accuracies_std = np.array([np.std(v) for k,v in sorted(k_to_accuracies.items())])
plt.errorbar(k_choices, accuracies_mean, yerr=accuracies_std)
plt.title('Cross-validation on k')
plt.xlabel('k')
plt.ylabel('Cross-validation accuracy')
plt.show()
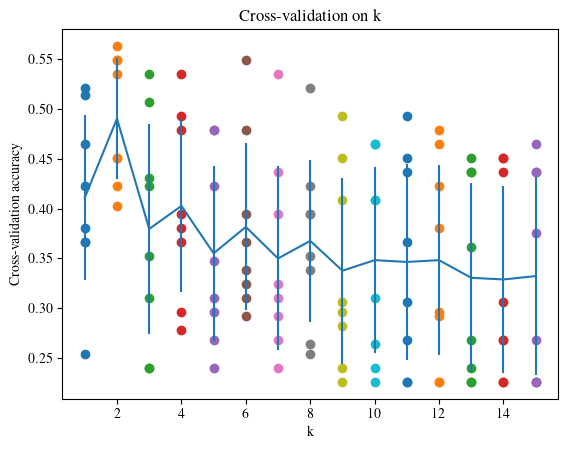
The Best Value for k¶
Based on the cross-validation results above:
choose the best value for k.
retrain the classifier using all the training data
test it on the test data
best_k = k_choices[accuracies_mean.argmax()]
print('Best value for k: ', best_k)
classifier = KNearestNeighbor()
classifier.train(X_train, y_train)
y_test_pred = classifier.predict(X_test, k=best_k, L=1)
# Compute and display the accuracy
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test
print('Got %d of %d correct => accuracy: %f' % (num_correct, num_test, accuracy))
Best value for k: 2
Got 113 of 168 correct => accuracy: 0.672619
